
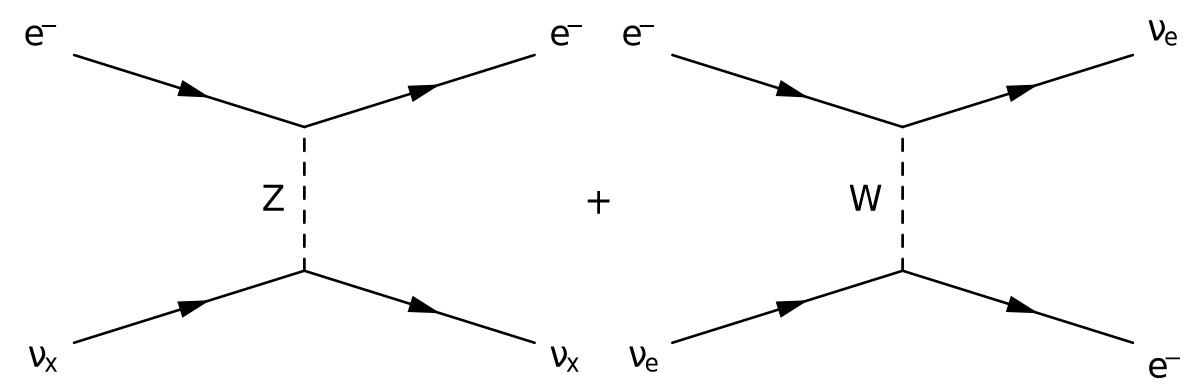
They could turn out to be identical to antineutrinos, their antimatter counterparts. Neutrinos could have other strange properties as well. It could be that neutrinos are the only fundamental particles that gain their mass from a source other than the Standard Model Higgs field. However, we know from oscillation experiments that neutrinos do have tiny masses. The Standard Model, the best description of the fundamental particles and forces that make up our universe, predicted that neutrinos would have no mass. They have puzzlingly low masses when compared to other elementary particles, and they are able to oscillate, or change from one type of neutrino to another. Neutrinos, first discovered in 1956, come in three flavors (or types) and have some mysterious characteristics.
Their odd properties could be a clue to a deeper understanding of the most fundamental physics in the universe, which is why Fermilab has put together a suite of world-leading experiments. While small and antisocial, neutrinos are the most abundant particle with mass in the universe - so the sheer number of them could have a powerful collective effect. Our universe is permeated with neutrinos - nearly massless, neutral particles that interact so rarely with other matter that trillions of them pass through our bodies each second without leaving a trace. The Long-Baseline Neutrino Facility will provide the neutrino beamline and the infrastructure that will support the DUNE detectors. Scientists will search for new subatomic phenomena and potentially transform our understanding of neutrinos and their role in the universe. Scientists will use giant detectors to study the neutrinos' travel patterns over that distance, recording neutrino interactions at either end of the journey. At Fermilab's flagship experiment DUNE, the Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment, the lab will send neutrinos 800 miles through Earth's mantle to a former gold mine in Lead, South Dakota. Before being detected, neutrinos from Fermilab experiments travel over short distances - several hundred meters - and over long distances - several hundred miles.įermilab is hosting what will be the largest experiment of its kind when complete: DUNE at LBNF. The lab's suite of experiments to study the subtle, elusive particle called the neutrino will aid humanity's understanding of the origin of matter, the unification of forces and the Big Bang. Science of matter, energy, space and timeįermilab is the neutrino capital of the world.Fermilab Accelerator Science and Technology Facility.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
